Vernacular Architecture in India:
Imagine walking through the vibrant streets of Rajasthan, where yellow sandstone buildings reflect the golden hues of the desert, or standing beneath the sloping tiled roofs of a traditional kerala home, perfectly designed to withstand heavy monsoons. These examples of vernacular architecture in India highlight how deeply intertwine design and environment can be. Rooted in local traditions and influenced by geographical, cultural, and climatic factors, vernacular architecture is a form of design that has stood the test of time.
In this blog we will explore the types of vernacular architecture, delve into its defining characteristics, highlight the beauty of Kerala vernacular architecture, and discuss the relevance of modern vernacular architecture in contemporary times.
What is Vernacular Architecture?
Vernacular architecture in India refers to structures designed and built by local craftsmen without the intervention of professional architects. These designs are shaped by the resources available in a region and the cultural practices of the people living there. Each structure reflects the ingenuity of adapting to the local climate and needs, making it highly efficient and functional.
Types of Vernacular Architecture in India
Vernacular architecture varies significantly across India, showcasing the diversity of human ingenuity. Some notable types include:
1.Desert Vernacular
Bhungas in Gujarat
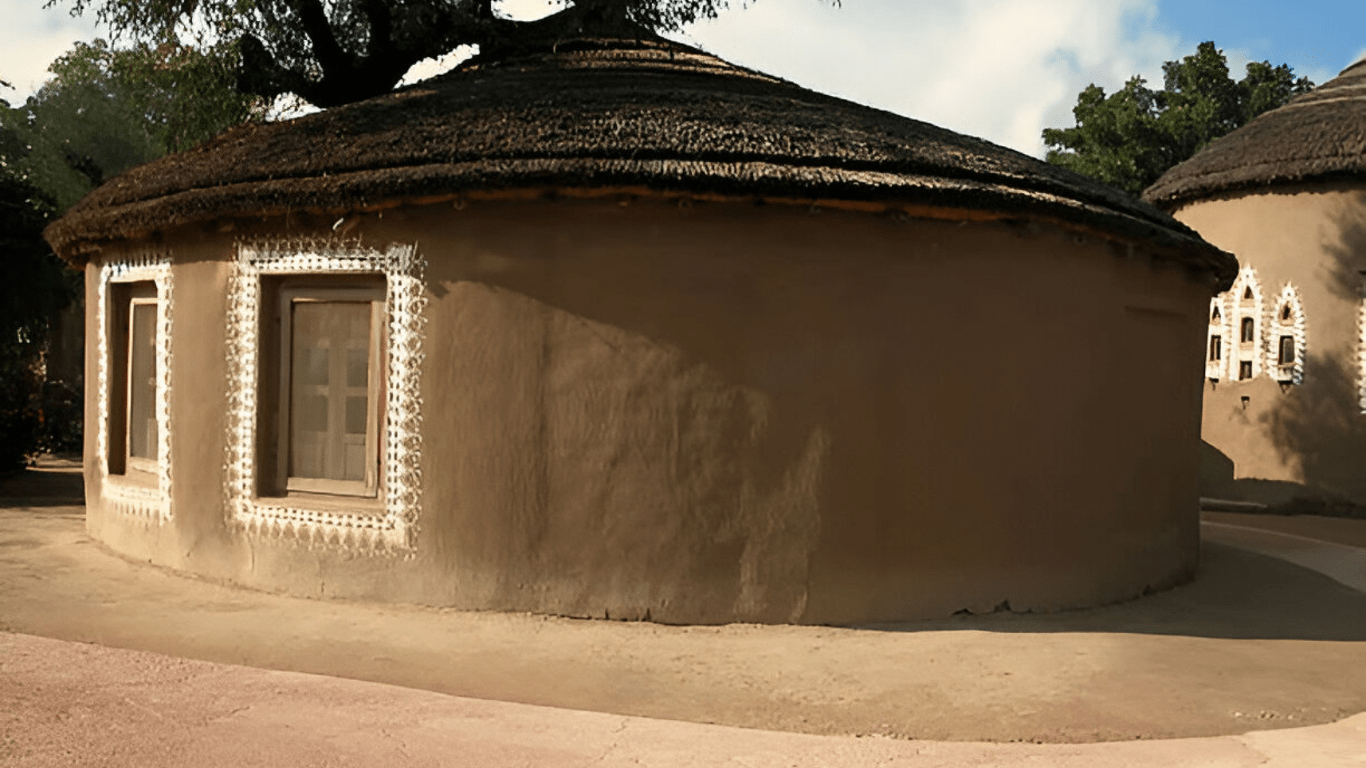

Found in arid regions, these structures use thick mud or stone walls to keep interiors cool.
2.Tropical Vernacular
Built for humid climates, these homes have elevated floors, large windows, and sloped roofs. Example:
Bamboo houses in Northeast India

3.Mountain Vernacular
Kath-Kuni architecture in Himachal Pradesh
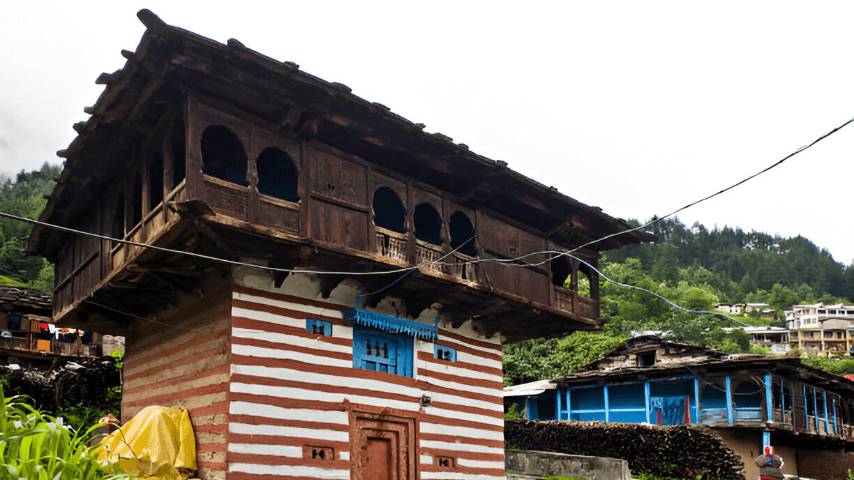

Designed to withstand harsh winters, these structures often use stone and wood. Example:
4.Coastal Vernacular
Kerala’s traditional houses
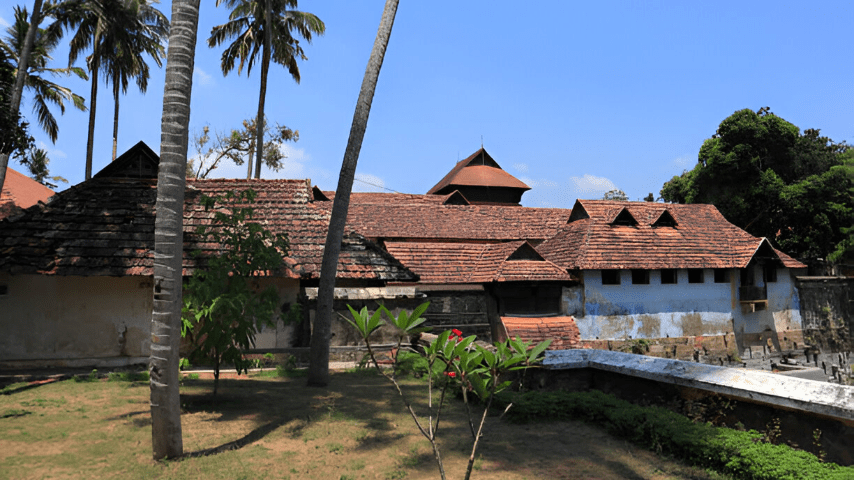

Adapted to withstand heavy rainfall and high humidity, these homes often feature thatched or tiled roofs
5.Plateau Vernacular
Wada in Maharashtra

Found in regions with moderate climates, these homes use materials like laterite and incorporate verandas for shaded living areas.
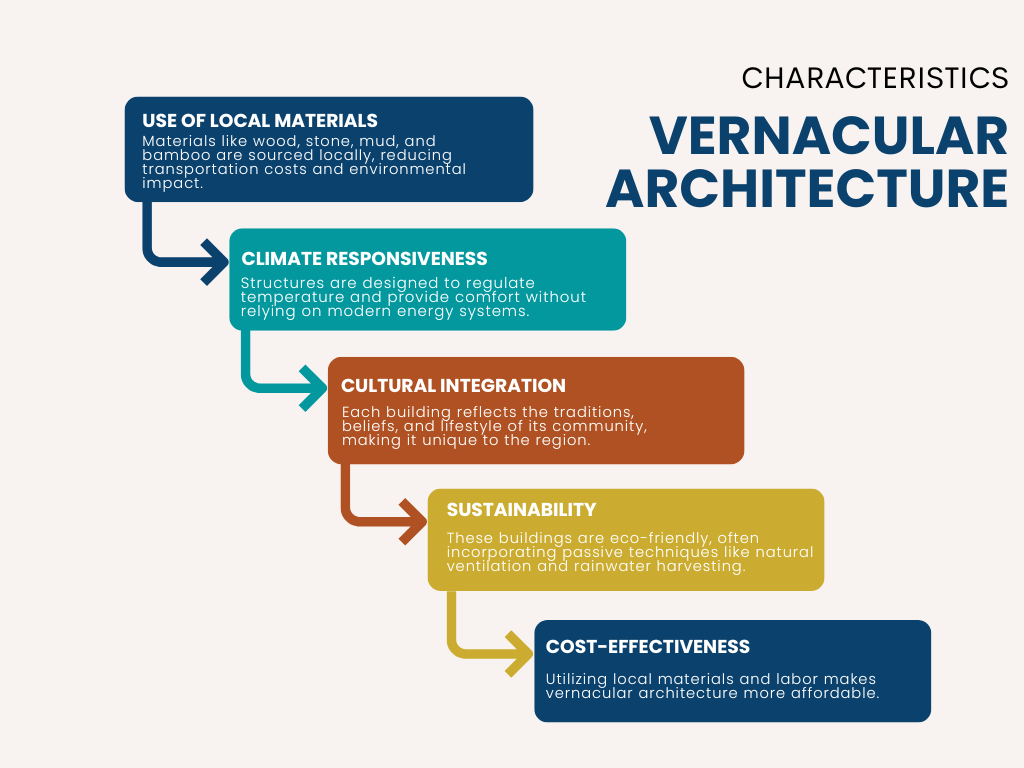
Vernacular Architecture Characteristics
Vernacular architecture in India stands out due to its distinct characteristics:
Kerala Vernacular Architecture: A Timeless Tradition
Kerala’s vernacular architecture is a stunning example of blending aesthetics with functionality. The traditional homes, called nalukettus, are designed with:

The design not only reflects the region’s cultural heritage but also ensures sustainability and harmony with nature.
What sets Kerala apart is its emphasis on harmony with the environment, creating structures that seamlessly integrate with the lush, tropical surroundings. In contrast, Rajasthan’s vernacular architecture adapts to a starkly different climate. Desert homes, such as those in Jaisalmer, use yellow sandstone and thick walls to keep interiors cool and protect against extreme heat. This comparison highlights the ingenuity of India’s vernacular styles, which adapt uniquely to their geographical and cultural contexts while ensuring sustainability.
Modern Vernacular Architecture: The Best of Both Worlds
Modern vernacular architecture in India combines traditional principles with contemporary techniques. It uses modern materials like concrete and steel while maintaining the essence of vernacular design. Key features include:
- Sustainable Practices : Incorporating solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient layouts.
- Cultural Relevance : Retaining traditional aesthetics while adapting to modern lifestyles.
- Innovative Use of Local Materials : Blending traditional materials like bamboo and clay with modern technologies for durability.
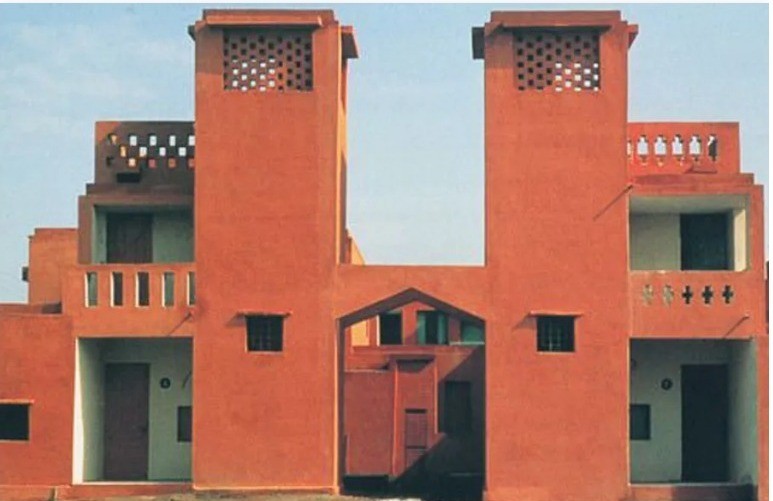

A notable example is the Aranya Low-Cost Housing project in Indore, designed by architect Balkrishna Doshi. This project demonstrates how vernacular principles can address modern urban housing needs while emphasizing sustainability and community living. Architects today are revisiting vernacular principles to create eco-friendly and culturally meaningful designs, addressing the challenges of urbanization without compromising on sustainability.
Why is Vernacular Architecture in India Important Today?
In an age where sustainability is paramount,vernacular architecture offers valuable lessons,It emphasizes:
- Eco-Friendly Construction - Reducing reliance on non-renewable resources
- Resilience: Structures built to withstand the climate challenges
- Cultural Preservation: Keeping traditions alive through architecture
As the world moves toward green living, the principles of vernacular architecture are being integrated into modern designs to create sustainable and harmonious environments.
Cibi+Simeon Designs: Top Architects in Chennai
Cibi+Simeon Designs are among the best architects in Chennai, known for their expertise in both modern and vernacular architecture. The innovative approach blends contemporary techniques with traditional principles, ensuring that every project is both sustainable and culturally resonant. Whether crafting sleek urban designs or eco-friendly spaces rooted in heritage, Cibi+Simeon Designs deliver exceptional architectural solutions tailored to their clients’ needs.
Conclusion
Vernacular architecture in India is more than just a building style; it is a testament to humanity’s ability to adapt and thrive. From the majestic Kerala vernacular architecture to innovative modern vernacular architecture, this approach continues to inspire. By revisiting traditional practices and integrating them with modern techniques, we can create spaces that are not only functional and beautiful but also sustainable and culturally rich. Embracing vernacular architecture in India is a step toward a greener and more meaningful future.