
TNCDBR 2019—Tamil Nadu Combined Development and Building Rules
Building regulations are essential to ensure that construction activities are carried out in a safe, efficient, and sustainable manner. They protect public health and safety, preserve the environment, and promote orderly urban growth. By setting clear guidelines for planning, design, and construction, building regulations help prevent structural failures, overcrowding, fire hazards, and other risks. They also play a vital role in supporting infrastructure planning, conserving resources like water and energy, and ensuring that buildings are accessible to all sections of society. In rapidly urbanizing regions like Tamil Nadu, which has implemented the “Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules 2019 (TNCDBR),” because strong building regulations are needed to achieve long-term development goals, encourage investment, and enhance the quality of life for residents.
Tamil Nadu Combined Development and Building Rules, 2019
What is TNCDBR?
TNCDBR, full form: Tamil Nadu Combined Development and Building Rules, 2019, aims to streamline building regulations for efficient land use and sustainable development in the state.
- The rules were issued on February 4, 2019, to replace existing building regulations.
- They focus on safety, security, and sustainability in urban planning.
- The rules incorporate provisions for accessibility, rainwater harvesting, and energy efficiency.
- They are based on international standards and local needs to promote affordable housing.
Structure of the Tamil Nadu Combined Development and Building Rules 2019
The Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building rules 2019 are organized into various parts detailing procedures, permissions, and regulations.
- The Tamil Nadu Combined Development rules are divided into seven parts, covering preliminary definitions, permission processes, development regulations, completion certificates, professional registrations, building rules, and specific forms.
- Each part addresses different aspects of building and development, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the subject.
Application and Permission Process
The rules outline the process for obtaining planning permission and building permits.
- Applications must be made in a specified format to the competent authority.
- Scrutiny fees are required for processing applications.
- The rules emphasize timely approvals and provide for deemed approvals if the authority fails to respond within a specified timeframe.
Development Regulations and Compliance
The rules set forth regulations to ensure developments conform to safety and planning standards.
- Developments must align with the Master Plan and zoning regulations.
- Specific parameters are established for different types of buildings, including high-rise structures and industrial facilities.
- Provisions for environmental sustainability, such as solar energy capture and water conservation, are included.
Building Safety and Structural Requirements
The rules emphasize the importance of safety and structural integrity in building design.
- Structural safety measures are mandated for all buildings, including high-rise constructions.
- Requirements for sanitation, stormwater drainage, and electrical installations are specified.
- Fire safety regulations include the installation of fire alarms and emergency exits.
Professional Registration and Responsibilities
The rules establish a framework for the registration of professionals involved in building and development. Architects, engineers, and other professionals must be registered and adhere to specified duties and responsibilities.
The rules outline the process for appointing professionals and the implications of changes in ownership or professional roles.
Compliance with these regulations is essential for maintaining standards in construction and development.
Forms and Documentation
The rules include various forms and documentation requirements for compliance and reporting.
- Specific forms are provided for applications related to land subdivision, building construction, and completion certificates.
- Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules, 2019 states that for proper documentation is required for progress reporting at different construction stages.
- The rules ensure that all necessary paperwork is standardized for ease of use and compliance.
Applicability of Building: Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules 2019
The rules apply to all forms of development and construction activities.
- These rules cover all developments, redevelopments, and alterations to buildings.
- They apply to changes in use or occupancy of buildings.
- Existing approved buildings are exempt from removal or alteration unless specified.
Written Permission for Development
No development can occur without written permission from the competent authority.
- Written permission includes electronic versions with digital signatures.
- Site approval does not exempt applicants from other legal requirements.
Competent Authority for Planning Permission
The authority responsible for issuing planning permissions varies by location.
- In Chennai, the Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority is the competent authority.
- In other areas, the appropriate planning authority designated by the Director is responsible.
Application Process for Planning Permission
The application process for obtaining planning permission is detailed and structured.
- Applicants must submit online applications with necessary documents.
- Certain government constructions are exempt from these rules.
- Applications must include proof of ownership and detailed plans.
Scrutiny Fees for Applications
Scrutiny fees are required for processing planning permission applications.
- Fees are calculated based on the area of the plans submitted.
- No fees are collected for residential projects for economically weaker sections.
Plan Requirements for Applications
Specific plans and documents are required for planning and building permits.
- Key plans must show site boundaries and neighborhood landmarks.
- Site plans must detail existing buildings and access routes.
- Building plans must include structural details and service locations.
Inspection Requirements During Construction
Inspections are mandatory at various stages of construction.
- Inspections ensure compliance with approved plans and regulations.
- Progress certificates must be submitted at key construction stages.
Sanctioning of Applications
The competent authority must sanction applications based on compliance with rules.
- Written permission is issued within 45 days if requirements are met.
- Applications can be rejected if they do not comply with regulations.
Limitations of Granted Permissions
Granted permissions do not absolve responsibility for various legal aspects.
- Title or ownership of the site is not guaranteed by the permission.
- Structural integrity and compliance with other laws remain the responsibility of the professionals involved.
Demolition of Buildings Regulations
Specific procedures must be followed for demolishing buildings.
- Applications for demolition must be submitted to the local authority.
- Demolition charges may apply as specified by the competent authority.
Cancellation and Renewal of Permits
Permits can be canceled or renewed under certain conditions.
- Permits obtained through misrepresentation can be canceled.
- Renewals are valid for an additional three years upon application.
Conformity of Developments with Rules
All developments must conform to the established rules and regulations.
- No construction can occur that violates these rules.
- Developments must align with the designated land use in planning documents.
Registration of Professionals in Construction
Professionals involved in construction must be registered and adhere to specific duties.
- Registration is valid for five years and requires a fee.
- Professionals must comply with local acts and regulations.
Development Regulations and Requirements
Specific regulations govern the development of buildings and land use.
- Structures must adhere to setback requirements and other spatial regulations.
- Special provisions exist for economically weaker sections and coastal regulation zones.
1. Natural Hazard Prone Areas Regulations
Natural hazard-prone areas are designated by the government based on various risks, and specific construction rules apply to these areas.
- Areas at risk include those prone to earthquakes, cyclones, floods, landslides, and tsunamis.
- The government will notify these areas periodically.
- Building designs must adhere to special provisions for hazard-prone areas.
2. Land Use Zones and Variations
Land use zones are defined and can be updated based on new information or variations.
- Different land use zones include residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural.
- Variations in land use must be published after approval of relevant plans.
3. Zoning Regulations Overview
Zoning regulations categorize land for specific uses and outline permissible activities.
- Categories include residential, commercial, industrial, and hazardous use zones.
- Activities permissible in each zone are detailed in an annexure.
4. Shelter Charges for Development Projects
Developers must provide affordable housing or pay shelter charges if their project exceeds a certain size.
- Projects over 4000 sq. m must allocate 10% of FSI for low-income housing or pay 1% of GLV as shelter charges.
- Housing units for low-income groups must be within 2 km of the project site.
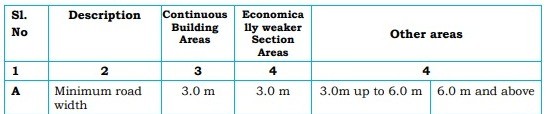
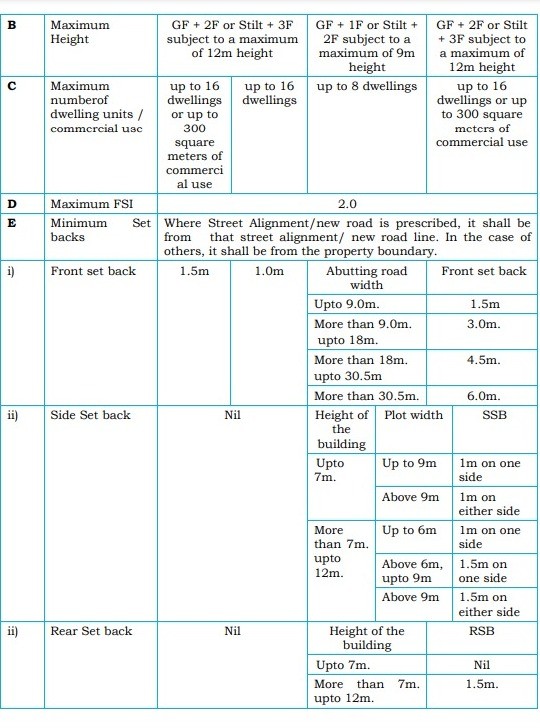
5. Planning Parameters for Non-High-Rise Buildings
Non-high-rise buildings have specific planning parameters regarding height, setbacks, and road width.
- Buildings up to 18.30 m must have a minimum road width of 3.0 m to 9.0 m depending on the area.
- Maximum height is 14 m for certain areas and 9 m for economically weaker sections.
- Setbacks vary based on building height and road width.
5. Planning Parameters for Industries
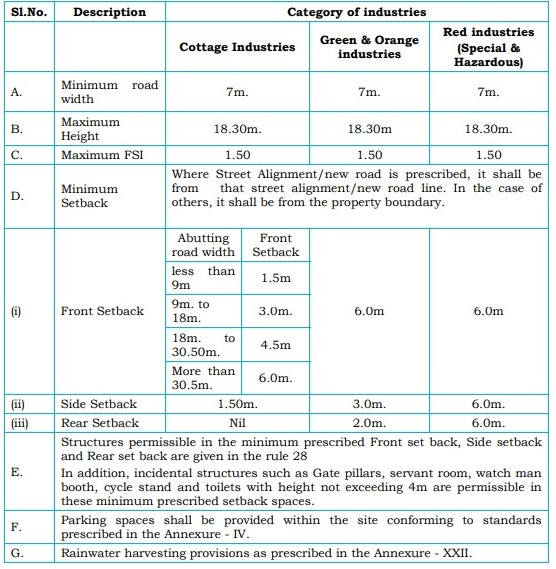
Industries are regulated by specific planning parameters, including road width and maximum height.
- Minimum road width for industries is 7 m, with a maximum height of 18.30 m.
- Maximum FSI is set at 1.50, with specific setback requirements.
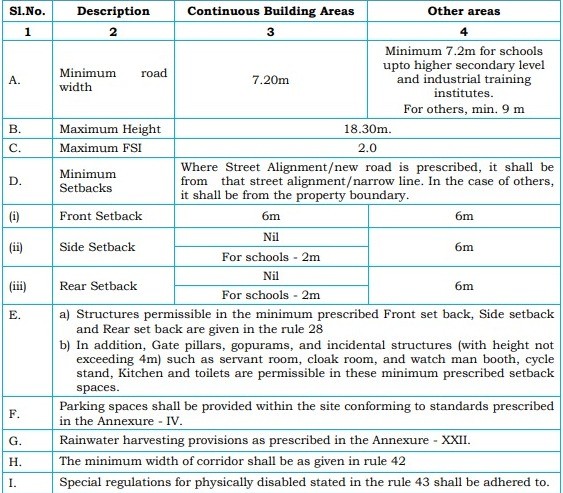
6. Planning Parameters for Institutional Buildings
Institutional buildings have defined parameters for road width, height, and setbacks.
- Minimum road width is 7.2 m, with a maximum height of 18.30 m.
- Maximum FSI is 2.0, and setbacks are required based on building type.

7. Planning Parameters for Transport Terminals
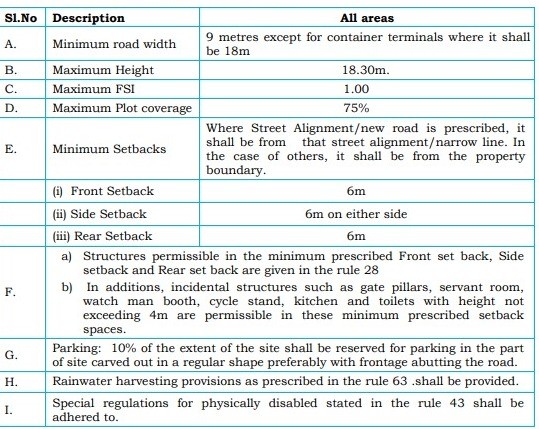
Transport terminals have specific requirements for road width, height, and setbacks.
- Minimum road width is 9 m, except for container terminals, which require 18 m.
- Maximum height is 18.30 m, with a maximum plot coverage of 75%.
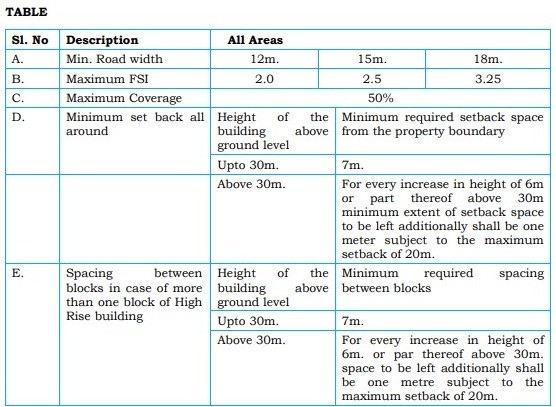
8. Special Rules for High-Rise Buildings
High-rise buildings have specific regulations regarding site access and planning parameters.
- Sites must be about roads of at least 18 m width or have exclusive access of the same width.
- Maximum FSI varies based on road width, with a maximum of 3.25 for 18 m roads.
9. Community Recreational Land Reservation
Developments must reserve land for community recreational purposes based on site size.
- No reservation is required for sites under 3,000 sq. m.
- For sites between 3,000 and 10,000 sq. m, 10% must be reserved, while sites over 10,000 sq. m require 10% with a minimum of 500 sq. m.
10. Corridor / Verandah width
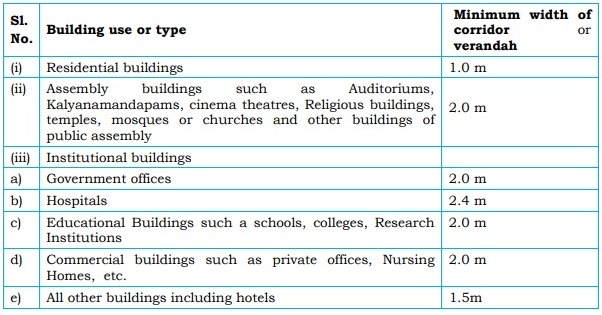
The minimum width of corridor or verandah within
buildings shall be as given below.
11. Provisions for Differently Abled Individuals
Buildings must be designed to be accessible for differently abled individuals.
- Access paths must be at least 1800 mm wide with a maximum gradient of 5%.
- Special provisions for ramps, lifts, and toilets must be included in public buildings.
12. Solar Energy Capture Regulations
Buildings must incorporate solar energy systems for sustainability.
- High-rise buildings must install solar water heating systems and photovoltaic panels.
- A minimum of 1/3 of the terrace area must be reserved for solar panels.
13. Wind Electricity Generator Development Guidelines
Wind electricity generators are permitted across various land use zones with specific requirements.
- Minimum land size for installation is 150 m x 150 m.
- Public road access must be at least 7 m wide, and no community land reservation is required.
i) Electrical Transformer Room Standards
Electrical transformer rooms must meet specific standards for safety and accessibility.
- Rooms must be located on the ground floor with a minimum area of 6 m x 4 m.
- The approach road to the electrical room must be at least 3 m wide.
ii) Electrical Room Specifications
The electrical room must adhere to specific construction and safety standards.
- Raised cement flooring with a cable duct of 450 mm width and 750 mm depth around the room.
- Flooring should slope towards the cable duct, which is covered with RCC slabs of at least 75 mm thickness.
- The radius of curvature for cable ducts at turns must be no less than one meter.
15. Open Space Requirements for Installation
Adequate open space is necessary for installation and access.
- A clear space of 10 m x 4 m or 5 m x 5 m open to the sky is required.
- An approach road of at least 3 meters in width must lead to the public road, preferably at the main entrance.
16. Fire and Rescue Services Standards
Transformers and substations must comply with fire safety regulations.
- No transformer should be located below the first basement or above the ground floor.
- Indoor transformers with more than 2000 liters of oil are prohibited.
- Transformers should be housed in fireproof rooms with adequate ventilation and emergency lighting.
17. Layout and Subdivision Rules
These rules ensure proper access and circulation in development areas.
- Minimum width of public streets: 7.2 m for residential and 9 m for industrial layouts.
- Service roads of at least 7 m width are required when abutting national or state highways.
- Clearances and dimensions for various types of streets and passages are specified.
18. Recreational Space Reservation
Land must be reserved for recreational purposes in layouts.
- No reservation for layouts up to 3000 sq. m; 10% reservation for layouts between 3000 sq. m and 10,000 sq. m.
- Above 10,000 sq. m, 10% of the area must be reserved, with no equivalent land cost accepted.
19. Transferable Development Rights (TDR)
TDR allows landowners to separate development potential from the land.
- Applicable for road widening, traffic infrastructure, and urban development.
- Rights are based on government provisions and can be transferred.
20. Premium FSI Regulations
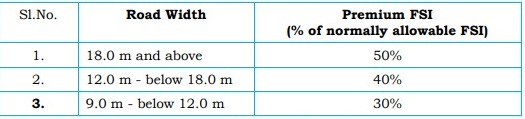
Premium Floor Space Index (FSI) can be obtained based on road width.
- 50% premium for roads 18 m and above, 40% for roads between 12 m and 18 m, and 30% for roads between 9 m and 12 m.
- Charges for premium FSI are based on guideline values.
21. Structural Safety Regulations
Structural safety measures are mandated for various building types.
- Non-high-rise buildings up to 12 m must have plans signed by a registered professional.
- Structural designs must conform to the National Building Code and relevant Indian Standards.
22. Building Requirements and Specifications
Specific requirements for different parts of buildings are outlined.
- Plinth height must be at least 45 cm above ground level.
- Outer walls must be constructed of incombustible materials, and damp-proof courses are required.
23. Sanitation and Sewerage Requirements
Sanitation facilities must meet minimum standards.
- Each dwelling unit must have at least one water closet and one kitchen sink.
- Septic tanks must conform to specific design and location requirements to prevent contamination.
24. Fire Safety Regulations
Fire safety measures are essential for all buildings.
- Buildings must have adequate exits and fire protection systems.
- High-rise buildings and public buildings require specific fire safety installations.
25. Telecommunication Structure Regulations
Telecommunication structures must comply with specific guidelines.
- BTS towers can be placed on rooftops or plots with proper access.
- Structural safety certificates are required for installations.
26. Water Conservation Measures
Rainwater harvesting and water conservation practices are mandated.
- Rainwater harvesting structures must be designed to recharge groundwater.
- Wastewater from baths and wash basins must be treated and reused for toilet flushing.
27.Tree Preservation and Heritage Conservation
Regulations are in place for tree preservation and heritage buildings.
- Tree Preservation Orders can be issued to protect specific trees or areas.
- Heritage buildings must conform to conservation rules to maintain their historical significance.
29. Planning Permission Application Process
The Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules 2019 outline the responsibilities and assurances of the landowner or developer when applying for planning permission for construction.
- The applicant must ensure construction aligns with the approved plan and agrees to demolish unauthorized additions.
- Open spaces and car parking must be maintained as per the approved plan.
- The applicant is jointly responsible for development charges and compliance with regulations.
- Premium FSI charges apply if the FSI exceeds permissible limits.
- The applicant must gift OSR areas or pay equivalent land costs as per regulations.
30. Consultant Engagement and Site Inspection
The Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules 2019 specifies the requirement for engaging qualified consultants for the proposed development and certifying site conditions.
- The applicant must engage an architect, structural engineer, geo-tech expert, and site supervision engineer.
- The architect certifies site measurements and compliance with road width and other parameters.
- The architect must inform the competent authority at crucial construction stages.
- Any deviations from the approved plan require prior approval from the competent authority.
Structural Safety and Compliance
The TNCDBR 2019 emphasizes the importance of structural safety and adherence to relevant codes and standards.
- The structural design must meet safety requirements for natural disasters as per the National Building Code.
- The site must be suitable for construction based on soil test reports.
- The construction must be supervised to ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
Sanitation and Parking Requirements
The TNCDBR outlines sanitation and parking requirements for various types of buildings and facilities.
- Specific sanitary unit requirements are provided based on occupancy type, including water closets, wash basins, and urinals.
- Parking requirements vary by building type, with detailed specifications for residential, commercial, and institutional uses.
- Off-street parking standards include dimensions for parking stalls and provisions for physically challenged individuals.
Protection Against Natural Hazards
The TNCDBR details measures for protecting buildings from natural hazards such as earthquakes and cyclones.
- Buildings in earthquake-prone areas must be designed to prevent soil liquefaction and ensure stability.
- Cyclone-prone structures require special design considerations for wind pressures and flooding.
- Recommendations include using deep foundations and ensuring proper drainage to mitigate flood risks.
Regulations for Special Provisions for Hospital Buildings
The TNCDBR 2019 specifies additional requirements for hospital buildings to ensure safety and accessibility.
- Ramps must be provided for accessibility, with specific width and slope requirements.
- Setback areas must be clear for firefighting access.
- Fire safety training and regular mock drills are mandated for hospital staff.
List of Industries and Environmental Classifications
The Tamil Nadu Combined Development Building Rules 2019 document categorizes various industries based on environmental impact and permissible activities.
- Industries are classified into categories such as “Green,” “Orange,” and “Red,” with specific examples listed for each.
- Green industries include low-impact activities like tailoring and handloom weaving.
- Red industries involve high environmental risks, such as chemical manufacturing and waste incineration.
Registration Criteria for Architects
Architects are registered in two grades based on qualifications and experience to ensure compliance with development rules.
- Architect Grade-I: Requires a B.Arch or equivalent degree with a minimum of 2 years of professional experience; can prepare plans for any type of building, including high-rise structures.
- Architect Grade-II: Requires a Diploma in architecture with 5 years of experience; can prepare plans for small developments as specified in the rules.
Duties and Responsibilities of Architects
Architects have specific duties to ensure construction compliance with approved plans and safety regulations.
- Responsible for ensuring work is executed per approved plans and NBC stipulations.
- Must obtain and submit necessary certificates and reports for occupancy and completion.
- Required to inform competent authorities of any deviations or changes in project status.
Special Regulations for Schools
Schools must adhere to specific regulations regarding site selection, building design, and safety measures.
- Sites should not be near highways, water bodies, or factories.
- Classrooms must meet minimum size and safety standards, including fire safety measures.
Conservation of Heritage Sites
Heritage sites must be preserved according to specific regulations to maintain their historical and cultural value.
- No alterations can be made without prior permission from the competent authority.
- The list of heritage buildings will be prepared and approved by the government in consultation with a Heritage Conservation Committee.
Maintaining Heritage Skyline and Development
This section emphasizes the importance of preserving the skyline of listed heritage buildings and precincts without allowing high-rise developments.
- Listed heritage buildings must maintain the existing skyline to preserve their value and beauty.
- Development within heritage precincts must follow guidelines set by the competent authority in consultation with the Heritage Conservation Committee.
Restrictions Imposed by Covenants
This section outlines the continuation of existing restrictions on leasehold plots imposed by various authorities.
- Existing restrictions under covenants by the state government, municipal corporation, and other bodies remain in effect.
- In case of conflict with heritage preservation interests, development regulations will take precedence.
Repair Fund for Heritage Buildings
This section discusses the establishment of a fund to assist in the repair of listed heritage buildings.
- Owners/lessees are responsible for repairs to their buildings.
- A separate fund may be created to assist owners who cannot afford repairs, managed by the Executive Authority in consultation with the Heritage Conservation Committee.
Grading System for Listed Heritage Buildings
This section introduces a grading system for listed heritage buildings and precincts, categorizing them into three grades.
- Grade-I: National or historical importance, requiring careful preservation.
- Grade-II: Regional or local importance, deserving intelligent conservation.
- Grade-III: Lesser importance, allowing for more changes while protecting unique features.
Composition of Heritage Conservation Committee
This section details the composition and responsibilities of the Heritage Conservation Committee outside the Chennai Metropolitan Area.
- The committee includes a district collector, representatives from PWD, state and central archeology, and other experts.
- The committee can co-opt additional members and has a tenure of three years for non-government members.
Development Restrictions in Prohibited Areas
This section outlines various areas where development is prohibited or restricted, including proximity to military and aviation facilities.
- No development within 100 m of Indian Air Force stations.
- Construction near airports requires compliance with civil aviation regulations and may need a no-objection certificate for buildings over 30 m.
Regulations for Aquifer Recharge Areas
This section specifies regulations for developments in aquifer recharge areas to protect water sources.
- Development is restricted to non-high-rise buildings up to 9 m in height.
- Permissible developments include residential buildings, schools, and parks, with specific area and height limitations.
Zoning Regulations Overview
This section provides an overview of zoning regulations for various use zones, including residential, commercial, and industrial.
- Residential zones allow for various residential types and small-scale commercial activities.
- Commercial zones permit all activities in residential zones plus larger commercial enterprises.
- Industrial zones allow for a wide range of industrial activities, excluding hazardous industries.
High-Rise Building Regulations in Chennai
This section outlines the areas where high-rise buildings are permissible in the Chennai Metropolitan Area.
- High-rise buildings are not allowed in specific areas, including the Island Grounds and aquifer recharge areas.
- Development regulations must be adhered to in designated high-rise zones.
Swimming Pool Construction and Operation Guidelines

This section details the regulations for constructing and operating swimming pools, including safety and design standards.
- Swimming pools must meet specific design criteria, including depth, slope, and safety features.
- Separate facilities for genders and compliance with health and safety standards are required.
- Regular inspections and a no-objection certificate are necessary for operation.
Fencing and Exits for Swimming Pools
All swimming pools must be securely fenced and have adequate exits for safety.
- Fencing must be at least 1.2 meters high and without hand or footholds.
- Poolside equipment should not enable climbing over the fence.
- A minimum of two exits, each at least 2.0 meters wide, must be located at opposite ends of the pool area.
Swimming Pool Water Treatment System
A comprehensive water treatment system is essential for maintaining pool water quality.
- The system must filter, chemically balance, and disinfect pool water with a turnover period not exceeding 6 hours.
- Hair and lint strainers must be installed on the suction side of the pump, with easily removable baskets.
- Inlets should ensure uniform water circulation and disinfectant residuals throughout the pool.
- Main drains must be designed to prevent bather entrapment and should be secured with tool-requiring grates.
Personnel Requirements for Swimming Pools
Qualified personnel are necessary for the safe operation and management of swimming pools.
- A competent pool manager is required for all pools and is responsible for safety and maintenance.
- Lifeguards must be present, with a minimum of one for pools up to 150 square meters.
- Swimming instructors must have appropriate certifications from recognized institutions.
- Lifeguards should not work more than 4 hours continuously and must have adequate rest periods.
Specific Safety Features for Pools
Safety features are critical for ensuring the well-being of pool users.
- Lifeguards must have a designated elevated chair for visibility and wear identifiable uniforms.
- Essential lifesaving equipment must be provided, including first aid kits, life jackets, and rescue devices.
- Safety instructions and emergency contact numbers should be clearly displayed around the pool area.
Water Quality Standards for Swimming Pools
Maintaining high water quality is vital for swimmer safety and comfort.
- Water clarity must allow visibility of a 4-inch object at the deepest point.
- pH levels should be maintained between 7.2 and 8.0, with free chlorine levels between 0.6 and 1.5 ppm.
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of the pool area are required to prevent disease transmission.
Operation and Maintenance Guidelines
Proper operation and maintenance are essential for pool safety and hygiene.
- The pool manager must ensure water cleanliness and change it at least every six months.
- Daily cleaning of pool decks and regular maintenance of equipment are mandatory.
- Security measures must be in place to control access to the pool area.
Regulations for Swimming Pool Users
Strict regulations govern who can use the swimming pool to ensure safety.
- Children under 8 years old or shorter than 121.6 cm must be supervised by an adult.
- Users must declare they are free from contagious diseases before entering the pool.
- Showering before pool entry is mandatory, and alcohol consumption is prohibited.
Application and Permission Process for Pools
A formal application process is required for constructing and operating swimming pools.
- Owners must submit detailed plans and obtain permission from the local authority before construction.
- Completion reports and compliance with safety standards are necessary for operational permits.
- Violations of rules can lead to suspension of permissions and penalties.
Norms for Non-High Rise Building : Tamil Nadu Combined Building Rules 2019

Regulations for non-high-rise buildings up to 18.30 m in height with specific criteria.
- The maximum increase in building dimensions is 0.30 meters in length and width.
- Setbacks can be reduced by 0.30 meters, with minimum setbacks of 1.20 meters or 0.80 meters depending on the original requirement.
- Height increase allowed up to 3% of approved height, not exceeding 18.30 meters, without adding an additional floor.
- The FSI tolerance limit is 0.03 of FSI or 50 sq. meters, whichever is higher.
- Changes in OHT location are allowed; development charges apply for size increases.
- Interconnection between flats is allowed if parking requirements are met.
- Column position changes are permissible without affecting a minimum 3.00-meter driveway.
- Changes in non-FSI area usage are allowed.
- If site measurements are less than approved but conform to rules, it is permissible.
- Entrance arches and pergolas are regulated as per rules.
- Rainwater harvesting is mandatory.
- Permanent compound walls must adhere to approved plans, with temporary fencing allowed for road widening areas.
- Fire licenses must comply with TNCBR provisions.
- No structures allowed on OSR land.
- Specific structures are permitted in setback areas, provided they meet parking requirements.
- Structures on terrace floors are limited to AC plants and two toilets per block.
- One-third of the terrace area must be reserved for solar panels, with 10 sq. meters needed for 1 KW of electricity.
Norms for High-Rise Buildings: Tamil Nadu Combined Building Rules 2019
Regulations for high-rise buildings with specific height and setback requirements.
- The maximum increase in building dimensions is 0.30 meters in length and width.
- Setbacks can be reduced by 0.30 meters, with a minimum of 6.70 meters for buildings up to 30 meters in height.
- Height increase was allowed up to 5% of approved height, with additional setbacks required on a pro rata basis.
- The FSI tolerance limit is 0.03 of FSI or 50 sq. meters, whichever is higher.
- Architectural projections and service ducts have specific width allowances and setback requirements.

- Changes in OHT location are allowed; development charges apply for size increases.
- Interconnection between flats is allowed if parking requirements are met.
- Column position changes are permissible without affecting a minimum 3.00-meter driveway.
- Changes in non-FSI area usage are allowed.
- If site measurements are less than approved but conform to rules, it is permissible.
- Entrance arches and pergolas are regulated as per rules.
- Rainwater harvesting is mandatory.
- Permanent compound walls must adhere to approved plans, with temporary fencing allowed for road widening areas.
- Fire licenses require a compliance certificate from DF&RS.
- No structures allowed on OSR land.
- Specific structures are permitted in setback areas, provided they meet parking requirements.
- Structures on terrace floors are limited to AC plants and two toilets per block.
- One-third of the terrace area must be reserved for solar panels, with 10 sq. meters needed for 1 KW of electricity.
Conclusion
2019Building regulations are essential for ensuring safe, sustainable, and well-planned urban development. They provide a structured framework that governs construction standards, land use, and design compliance, protecting the interests of both individuals and the community. By adhering to regulations like the Tamil Nadu Combined Development and Building Rules 2019(TNCDBR), stakeholders can contribute to organized growth, environmental conservation, and enhanced quality of life. Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, or developer, understanding and following building regulations is a critical step toward responsible construction and future-ready infrastructure.
Source: TNCDBR, 2019
About Author
At Cibi + Simeon Designs—the best architectural designers in Chennai—we don’t just draw blueprints; we bring your vision to life.
From architectural design and construction process to project management services and regulatory approvals, we guide you through every stage of your house construction journey. Our team will ensure that your project is in line with your budget, lifestyle, and space requirements.
We know that building a home is an investment you will make only once in your lifetime. We prioritize:
- Space Planning & Aesthetic Design
- Vastu home plan
- Budget alignment & accurate cost estimation.
- Transparent material selection


